A slow-loading website increases bounce rates, hurts conversions, and reduces your visibility in search results. Even a one-second delay can reduce conversion rates by 20% and erode user trust, especially on mobile, where expectations are higher and patience is lower.
Google evaluates website performance based on user experience signals. Core Web Vitals, such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and First Input Delay (FID), directly influence rankings, crawl efficiency, and engagement across devices.
When pages lag, users drop off before they see your offer. This results in lost leads, lower ROI from paid channels, and increased acquisition costs. The longer it takes to load, the more opportunity you lose.
At Los Angeles Public Relations (LAPR), we engineer performance from the ground up. Our optimization framework is built to improve technical speed, search rankings, and business outcomes, so your site loads fast, performs consistently, and converts better.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are the Most Effective Ways to Optimize Website Speed?
Site speed is determined by how efficiently your pages load, not just by their size. It’s shaped by the sequence in which resources are requested, parsed, and rendered in the browser.
The most effective optimizations restructure that sequence. They streamline how code executes, reduce what blocks rendering, and prioritize what appears first. When each layer supports the next, performance improves across both UX and search.
Minify and Compress Site Code
Every unnecessary line of code slows down your site. Minification removes whitespace, comments, and redundant characters from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript without changing functionality. Compression reduces file sizes further during transmission, improving parse and load times.
We use proven techniques like:
- HTML minification to strip markup noise
- CSS bundling to reduce stylesheet requests
- JavaScript tree shaking to eliminate unused functions
Before & After Minification (Example):
| File Type | Original Size | After Minification |
| HTML | 85KB | 28KB |
| CSS | 140KB | 42KB |
| JS | 220KB | 65KB |
After minification, we apply GZIP or Brotli compression, cutting transfer sizes by up to 80%. This immediately improves server response and reduces total load time.
Eliminate Render-Blocking Scripts with Async/Defer
When you place JavaScript and CSS in the <head> section, it often acts as render-blocking resources, preventing the browser from displaying content until scripts are fully loaded. This delays First Paint and Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), both critical Core Web Vitals metrics tied to UX and SEO.
To fix this, we defer non-critical scripts and load async-compatible ones:
| <!– Unoptimized –><script src=”main.js”></script><!– Optimized with defer –><script src=”main.js” defer></script><!– Optimized with async –><script src=”analytics.js” async></script> |
Use “defer” for scripts that control layout or interactivity, and “async” for analytics and non-essential tools. This reduces interactivity lag and allows the browser to focus on rendering visible content first.
Bundle Assets to Reduce HTTP Requests
Every individual CSS file, JavaScript module, font, or image creates a new HTTP request. On high-traffic pages, this slows down initial paint time and bloats the loading sequence.
To improve asset delivery:
- Bundle CSS and JS into single, minified files
- Preload fonts and key visuals for faster First Paint
- Use SVG sprites instead of separate icon files
- Inline critical CSS for above-the-fold content
Bundling reduces server chatter. Preloading prioritizes key resources. Together, they streamline load paths and enhance the speed at which your site becomes usable.
Defer Offscreen Media to Reduce Load Time
Non-critical media, such as images, videos, or iframes placed below the fold, shouldn’t load during the initial render. Loading them too early increases payload and delays user interaction.
Deferring offscreen media improves Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and reduces layout shifts by allowing above-the-fold content to render first. Native lazy loading, supported in most modern browsers, offers a reliable default.
Use loading=”lazy” on images and iframes that aren’t immediately visible. This reduces initial resource demand, helping the browser prioritize key content.
Compress Text-Based Assets to Improve TTFB
After minifying files, compression shrinks their size during transfer. This speeds up Time to First Byte (TTFB) and shortens overall load time, especially on slower connections.
Both GZIP and Brotli are widely supported and effective for text-based files like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Brotli generally achieves higher compression rates, though GZIP offers broader fallback compatibility.
Compression should be applied at the server level via Apache, NGINX, or CDN configuration, ensuring all eligible assets are delivered efficiently.
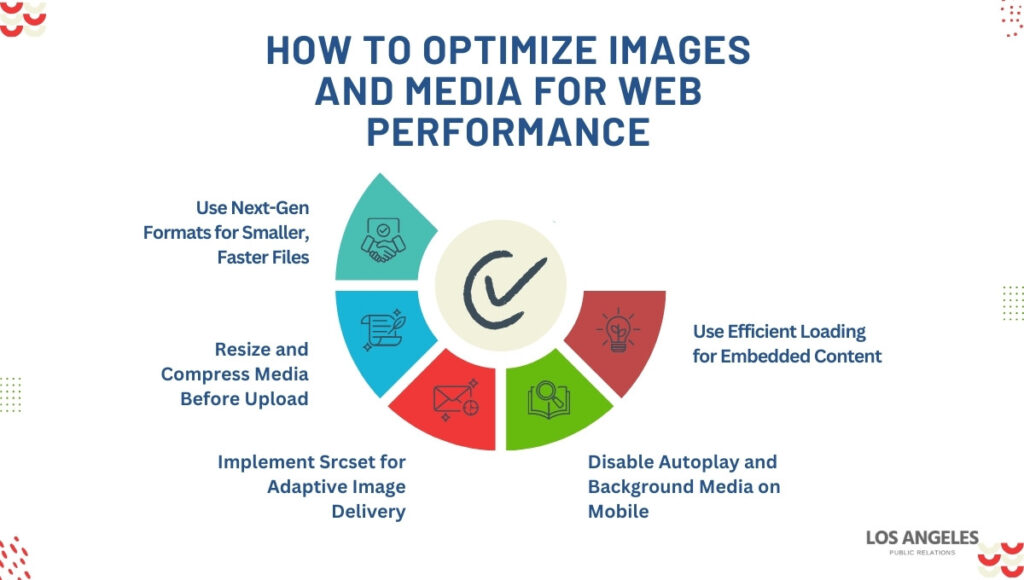
How to Optimize Images and Media for Web Performance
Images and media often account for the largest share (i.e., over 70%) of a page’s weight. If they’re not optimized, they can dominate network requests, increase load times, and negatively impact Core Web Vitals. Improving media performance means delivering only what’s needed, in the right format and resolution, at the right moment.
The most effective strategies combine lightweight formats, controlled delivery behavior, and context-aware rendering. Done correctly, they reduce page weight, improve mobile responsiveness, and shorten time-to-interaction without compromising quality.
Use Next-Gen Formats for Smaller, Faster Files
Modern formats like WebP and AVIF provide higher compression and visual fidelity than legacy JPEG or PNG. AVIF delivers the smallest file sizes for most images, though WebP offers broader compatibility.
Implement <picture> elements with fallbacks to ensure older browsers still receive a supported format.
| Format | Avg. Size Reduction vs. JPEG | Browser Support |
| WebP | 25-35% | Chrome, Safari, Edge |
| AVIF | 40-50% | Chrome, Firefox, Safari (partial) |
Smaller files load faster, use less bandwidth, and improve LCP, particularly on mobile devices.
Resize and Compress Media Before Upload
Uploading oversized images or raw video forces the browser to process more data than necessary, which can lead to slower performance. Match media dimensions to their display size and compress files before they ever reach the server.
Recommended baselines:
- Hero images: ≤ 200 KB
- Thumbnails: ≤ 50 KB
- Background videos: ≤ 1 MB (disabled on mobile)
Pre-upload optimization reduces the work for both your server and your user’s device, improving responsiveness.
Implement Srcset for Adaptive Image Delivery
The srcset and sizes attributes enable browsers to select the most suitable image file based on screen size and resolution. This ensures users on smaller screens or slower connections aren’t downloading unnecessarily large files.
| <img src=”image-800.jpg” srcset=”image-400.jpg 400w, image-800.jpg 800w, image-1200.jpg 1200w” sizes=”(max-width: 600px) 400px, (max-width: 900px) 800px, 1200px” alt=”Responsive example”> |
- srcset defines available image variants by width.
- Sizes tells the browser how much screen space the image will occupy.
- The browser selects the best file to load for the device context.
Adaptive delivery conserves bandwidth and accelerates rendering across devices.
Disable Autoplay and Background Media on Mobile
Autoplay video and background animations increase page weight and consume mobile bandwidth before the user interacts with the content. Disabling them on smaller viewports improves load time and reduces distractions.
Mobile-first adjustments:
- Replace autoplay with click-to-play
- Serve lower-resolution versions on mobile
- Disable background video below 768px viewport
- Hide heavy animations unless triggered by the user
These changes make mobile sessions faster, lighter, and more user-friendly.
Use Efficient Loading for Embedded Content
Third-party media embeds (such as maps, social feeds, and video players) often load scripts and assets that aren’t visible on initial render. Load them only when needed, either via click-to-load or after a user scrolls near the embed.
This prevents hidden media from competing with above-the-fold assets during initial load, improving both LCP and First Input Delay (FID).
How to Measure and Benchmark Your Website Speed
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Without reliable benchmarks, it’s impossible to pinpoint where performance drops or prove the business impact of addressing the issue.
Effective speed measurement blends field data (real-user experience) with lab data (controlled tests). Field data shows how your site performs across devices, networks, and geographies. Lab data isolates technical bottlenecks you can fix directly.
At LAPR, we use both to build an accurate performance baseline, then track gains after every optimization.
Track Core Web Vitals in Field and Lab Environments
Google’s Core Web Vitals define how speed, responsiveness, and stability are measured for SEO and UX. Each metric has specific thresholds for what’s considered good, needs improvement, or poor.
| Metric | Category | What It Measures | Good | Needs Improvement | Poor |
| TTFB | Loading | Time from request to first byte received | ≤200 ms | 201-600 ms | >600 ms |
| FCP | Loading | Time to first pixel rendered | ≤1.8 s | 1.9-3.0 s | >3.0 s |
| LCP | Loading | Time to render the largest visible content block | ≤2.5 s | 2.6-4.0 s | >4.0 s |
| FID | Interactivity | Delay between first user input and response | ≤100 ms | 101-300 ms | >300 ms |
| CLS | Visual Stability | Amount of unexpected layout shift | ≤0.1 | 0.11–0.25 | >0.25 |
Field tools, such as the Chrome User Experience Report and Google Search Console, reveal how real visitors perform on these metrics. Lab tools like Lighthouse and WebPageTest simulate conditions to uncover root causes.
Use Multiple Tools for a Complete Speed Profile
No single platform captures the full picture of performance. Combining tools gives you both technical insights and real-user context.
| Tool | Key Strengths | Data Type | Use Case |
| PageSpeed Insights | Real-world Core Web Vitals (CrUX), field data | Field (RUM) | Measure actual user experience |
| GTmetrix | Waterfall analysis, historical trends | Lab | Track bottlenecks, compare changes |
| WebPageTest | Multi-location, multi-device testing, filmstrip rendering | Lab + Filmstrip | Visual load timeline, geo insights |
Cross-referencing results from these tools ensures that measurements are accurate, actionable, and relevant to both users and search engines.
Benchmark and Track Website Speed Targets for 2025
Core Web Vitals measure specific interaction points, but full-page load time is equally critical for SEO, conversions, and engagement. Aim for these 2025 performance targets:
| Device | Good (Fast) | Acceptable | Poor (Slow) |
| Mobile | ≤2.5 seconds | 2.6–4.0 seconds | >4.0 seconds |
| Desktop | ≤1.8 seconds | 1.9–3.0 seconds | >3.0 seconds |
Benchmarking process:
- Record current Core Web Vitals and total load times for mobile and desktop.
- Log business KPIs: conversions, bounce rates, engagement time, alongside performance scores.
- Retest after each optimization to determine if the results meet or exceed the targets.
- Use the comparison data to decide which fixes deliver the most ROI.
Consistently measuring against these targets keeps your site fast, competitive, and aligned with user expectations.
Monitor Continuously to Catch Regressions
Site speed declines over time due to code changes, new media, or the addition of third-party scripts. Use monitoring platforms like Calibre, SpeedCurve, or New Relic Browser to:
- Trigger alerts when metrics drop below thresholds
- Compare performance by device and geography
- Track month-over-month trends
Consistent monitoring safeguards both rankings and user experience.
How Does Hosting Impact Website Speed and Server Response Time?
Your hosting setup sets the baseline for site performance. A slow or overloaded server increases Time to First Byte (TTFB), network latency, and the risk of downtime, even if your front-end is optimized.
The fastest sites run on hosting with high CPU performance, fast I/O, and low-latency networks, ensuring quick execution, stable uptime, and consistent speed under load.
Use VPS or Cloud Hosting for Dedicated Speed Gains
Shared hosting divides CPU and memory resources across multiple sites, often resulting in throttling during peak usage. This raises TTFB and slows delivery.
Better options:
| Hosting Type | Resource Allocation | Performance Impact | Ideal For |
| Shared | Shared with many users | Prone to slowdowns, limited control | Small, low-traffic sites |
| VPS | Dedicated virtual resources | Stable TTFB, better scalability | Growing businesses |
| Cloud | Elastic, distributed resources | High availability, lowest latency | Enterprise and high-traffic sites |
For SEO- and UX-critical sites, VPS and cloud hosting consistently outperform shared plans in both response time and uptime.
Enable Server-Side Caching for Dynamic Content
Dynamic pages retrieve data from the database on every request, which slows down delivery. Server-side caching stores rendered HTML or reusable fragments, cutting generation time.
Caching options that improve performance:
- Full-page caching: Stores complete HTML output.
- Fragment caching: Saves repeated UI components.
- Object caching: Keeps database query results in memory.
- Caching headers: Guides browser and proxy behavior.
Tools like Varnish or Redis can reduce response times for both repeat and new visitors.
Choose Fast DNS and Optimized Server Architecture
Slow DNS resolution adds milliseconds before the browser can even connect to your server. Once the connection is made, your server’s hardware and protocol support determine how quickly the first byte is sent.
DNS + server performance checklist:
- Low-latency DNS provider (e.g., Cloudflare, Google Public DNS)
- Server location close to the primary user base
- SSD or NVMe storage for fast disk I/O
- HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 enabled for parallel, efficient delivery
- High concurrent connection capacity for traffic spikes
By optimizing both DNS lookup times and server infrastructure, you shorten connection handshakes, improve TTFB, and maintain fast delivery even under load.
How Do CDNs Accelerate Website Loading Across Locations?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) speeds up page delivery by serving content from servers located closer to your audience. These edge nodes reduce travel distance, cut latency, and ease the load on your origin server. When configured correctly, a CDN improves Time to First Byte (TTFB), stabilizes global performance, and maintains speed during traffic spikes.
Use Edge Nodes to Minimize Global Latency
CDN edge nodes are geographically distributed servers that cache or proxy content closer to the end user. Unlike origin servers, which may be located thousands of miles away, edge nodes serve content locally, reducing latency, network hops, and page load times.
For example, a user in Tokyo accessing content from a U.S. origin might experience 250ms latency, while an edge node in Japan can reduce this to under 50ms. Similar improvements apply across the EU, LATAM, and Asia, making edge delivery essential for consistent global performance.
| Edge Delivery Architecture Illustration:User → Local Edge Node → (If cached) Instant Content → (If not cached) Fetch from Origin |
Cache Static Files to Reduce Server Load
A CDN can cache static content like images, JavaScript, and CSS at edge nodes to eliminate unnecessary round-trips to your origin server. This reduces load on infrastructure, improves cache hit ratio, and enhances repeat visit performance by serving files instantly from local nodes.
Freshness is managed using cache headers and TTL (Time-to-Live) directives, which instruct browsers and CDNs on how long to store assets before revalidation.
| Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000, immutable |
This setup enables long-term static asset caching, reducing server load and improving user experiences across the site.
Optimize CDN Routing Based on User Proximity
Modern CDNs utilize intelligent routing to deliver content via the fastest, least congested path. Technologies like anycast and smart DNS dynamically route requests based on user location, network health, and real-time traffic conditions, maximizing speed and reliability.
This level of CDN routing optimization ensures that users in different regions receive content from the nearest, most responsive edge node, even during outages or spikes in demand.
| Comparative Routing Path Example:User in Tokyo → Tokyo Edge Node → Origin (if needed) User in LA → LA Edge Node → Origin (if needed) |
Dynamic rerouting reduces latency, prevents bottlenecks, and maintains consistent page delivery under varying network loads.

Which Tools and Plugins Affect Page Load Time Positively or Negatively?
The tools you install can either streamline page delivery or quietly sabotage it. Every plugin, theme, or script adds code that must load, parse, and execute, and the way that code behaves directly affects Core Web Vitals.
Well-optimized plugins use lightweight assets, defer non-critical scripts, and integrate cleanly with your caching strategy. Poorly built ones trigger render-blocking behavior, inflate DOM size, and increase Time to First Byte (TTFB). Evaluating impact at the plugin level is one of the fastest ways to stabilize performance.
Boost Page Speed with WP Rocket and LiteSpeed Cache
WP Rocket and LiteSpeed Cache consistently rank among the most effective performance plugins for WordPress. Both handle page caching, asset minification, and preload optimization — directly improving metrics like LCP, FID, and TTFB.
| Feature | WP Rocket | LiteSpeed Cache |
| Page Caching | Yes | Yes |
| CSS/JS Minification | Yes | Yes |
| Critical CSS Generation | Built-in | Requires QUIC.cloud |
| Preload Support | Sitemap & DNS prefetch | Object & image preloading |
| Host/CDN Compatibility | Universal | Best on LiteSpeed servers |
WP Rocket is a universal choice for most hosting environments, while LiteSpeed Cache unlocks maximum gains on LiteSpeed-based servers. Both deliver measurable improvements when paired with a fast host and a well-configured CDN.
Improve CSS/JS Performance with Autoptimize and Asset CleanUp
Autoptimize and Asset Cleanup provide granular control over how CSS and JavaScript load, which is critical for reducing render-blocking behavior. These tools combine, minify, and defer scripts so browsers can render above-the-fold content sooner.
Before Optimization (Render-blocking JS):
| <script src=”jquery.js”></script><script src=”theme.js”></script> |
After Optimization (Deferred + Combined):
| <script src=”combined.min.js” defer></script> |
Both plugins can generate critical CSS and unload unnecessary assets on a per-page basis, thereby shrinking the payload and reducing HTTP requests, which accelerates First Paint and improves the overall user experience.
Avoid Page Builders Like Elementor & Divi That Add Front-End Bloat
Visual page builders like Elementor and Divi deliver design flexibility but often at the cost of speed. Their large CSS bundles, inline styles, and JavaScript dependencies inflate DOM size, extend load times, and lower Core Web Vitals scores.
| Builder | Total Page Size | DOM Elements | FID Score |
| Elementor | 2.3 MB | 1,900+ | Poor |
| Divi | 2.0 MB | 1,700+ | Poor |
| Custom HTML/CSS | 850 KB | <600 | Good |
If your brand relies on SEO performance, high conversions, and a responsive UX, consider custom-coded templates or aggressively optimize builder output with selective asset loading and code cleanup.
How to Track and Maintain Long-Term Website Speed
Website speed is not a one-time optimization; it’s a performance signal that shifts over time with code updates, content growth, and infrastructure changes. Without consistent tracking, slowdowns often go unnoticed until rankings drop or conversions decline.
Long-term stability depends on combining continuous monitoring, scheduled audits, and proactive alerts to identify and address regressions before they impact user experience.
Monitor Site Speed with RUM and Synthetic Tools
Accurate monitoring requires two perspectives:
- Real User Monitoring (RUM): captures actual user interactions under live network and device conditions.
- Synthetic testing: simulates page loads in controlled environments to catch regressions before deployment.
| Tool | Method | Data Freshness | Best Use Case |
| Pingdom | Synthetic | On-demand | Pre-deploy load validation |
| SpeedCurve | Hybrid (RUM + Synthetic) | Continuous | Ongoing UX performance tracking |
| Lighthouse CI | Synthetic | CI-based | Detecting code-level regressions |
| New Relic | RUM | Real-time | Live user behavior analysis |
Using both methods ensures that you see how real users experience your site and how it performs under ideal test conditions, providing actionable insights at every stage of the development lifecycle.
Conduct Quarterly Audits and Regression Tests
Schedule a full speed audit every 90 days to measure current performance against your established baseline. This keeps slowdowns from creeping in unnoticed.
Quarterly Website Speed Testing Checklist:
- Compare TTFB and LCP to previous benchmarks
- Check for JavaScript bundle growth or unused scripts
- Audit the total request count and third-party dependencies
- Review CLS shifts caused by layout changes
- Validate overall Core Web Vitals against prior results
Regression tests identify the impact of code changes, plugin updates, and content expansion, so you can act before users experience slowdowns.
Set Up Alerts for Core Web Vitals Thresholds
Automated alerts detect speed regressions as soon as they occur. Tools like Google Search Console, Cloudflare Analytics, and SpeedVitals track LCP, CLS, and FID in real time.
Trigger alerts when:
- LCP > 2.5s
- CLS > 0.1
- FID > 100ms
Sample CWV Alert Workflow:
| SpeedVitals → Detects CLS spike → Triggers Alert → Sends to Slack/email → Team notified → Issue logged in project tracker |
Linking alerts to Slack, email, or task managers ensures no performance issue goes unresolved. Proactive detection ensures that UX and SEO remain intact even as your site evolves.
How Can UX Design Support Website Performance Optimization?
UX decisions influence how quickly a site renders as much as back-end code or server configuration. Choices in typography, layout, interaction patterns, and navigation structure determine how efficiently the browser can load, compile, and paint content.
Designing for speed means planning performance into the interface from the start, so every visual choice supports Core Web Vitals and reduces perceived wait time.
Use System Fonts and Font-Display for Faster First Paint
System fonts load instantly because they already exist on the user’s device, eliminating the need for network fetches. Adding font-display: swap ensures text remains visible while custom fonts load, preventing the Flash of Unstyled Text (FOUT).
| font-family: system-ui, -apple-system, sans-serif;font-display: swap; |
Visual Comparison:
| Without font-display: swap | With font-display: swap |
| Text invisible until font loads | Text visible instantly with fallback |
This combination preserves legibility, improves First Contentful Paint (FCP), and maintains a low perceived load time, especially on mobile devices and slow connections.
Design Mobile-First UX with Minimal JavaScript
Mobile-first design improves speed by simplifying layouts, reducing script execution, and limiting heavy animations. A JS-light approach also lowers main-thread work, improving input responsiveness.
Performance-focused mobile UX tips:
- Collapse or hide secondary content by default
- Load scripts conditionally based on viewport size
- Avoid animation-heavy sliders or carousels
- Use simple, stacked layouts to reduce layout shifts
- Prioritize tap targets and fast input feedback
These adjustments shorten rendering cycles and deliver faster interactions on mobile-first user journeys.
Simplify Layouts for Faster Rendering
Overly complex layouts with deep DOM nesting or multiple wrapper layers increase rendering cost and memory use. Flattening the structure speeds up DOM parsing and reduces repaint triggers.
Deep Nesting Example (Before):
| <div class=”wrapper”> <div class=”section”> <div class=”grid”> <div class=”column”> <p>Text</p> </div> </div> </div></div> |
Flattened Layout (After):
| <section> <div class=”column”> <p>Text</p> </div></section> |
Simpler layouts improve CLS and FCP while making CSS rendering paths shorter and more predictable.
Structure Internal Linking for Crawl and Render Efficiency
Poorly planned internal linking can slow rendering and limit discoverability. Deeply nested pages, JS-only navigation, and orphaned content waste both user time and crawl budget.
Best practices for internal linking & UX speed are:
- Use a clear top-down hierarchy with logical parent-child paths
- Keep navigation depth to three clicks or fewer from the homepage
- Use HTML anchor tags instead of JS-only links
- Ensure all key pages are linked at least once
- Write descriptive anchor text for context and SEO
A streamlined linking structure helps browsers and crawlers reach content faster, supporting both UX clarity and SEO performance.
Why Website Speed Matters for SEO, Branding, and PR Success
In digital PR and brand strategy, website speed is more than a technical metric; it’s a trust signal. When a site lags, it frustrates journalists, partners, and customers at the very moments when attention matters most. Speed influences how your brand is perceived, how widely your content is discovered, and how effectively campaigns convert interest into action.
Slow Page Speed Increases Bounce Rate and Reduces Lead Generation
Every extra second a page takes to load increases the chance a user will leave before engaging. Delayed form rendering, shifting layouts, and sluggish above-the-fold visuals push visitors away and reduce lead submissions.
Speed-to-Bounce Benchmark
- Bounce rate rises 32% when load time exceeds 3s.
- Pages over 5s see 40%+ bounce rates.
- A 1s delay can cut conversions by up to 20%.
Common Drop-Off Triggers:
- Delayed interactivity on form or CTA elements
- Layout shifts that push visible content down
- Slow-loading hero content or above-the-fold visuals
Optimizing speed keeps users engaged long enough to complete key actions, improving both lead capture and campaign ROI.
Core Web Vitals Are Ranking Signals for Search Visibility
Google uses Core Web Vitals to measure a page’s loading speed, responsiveness, and visual stability, all factors that directly affect rankings. Pages that fail to meet these thresholds are more likely to lose visibility, especially on mobile searches.
Core Web Vitals Thresholds and SEO Impact
| Metric | Good | Needs Improvement | Poor | SEO Impact |
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | ≤ 2.5s | 2.6-4.0s | >4.0s | Affects perceived load speed |
| FID (First Input Delay) | ≤ 100ms | 101-300ms | >300ms | Influences input responsiveness |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | ≤ 0.1 | 0.11-0.25 | >0.25 | Impacts visual stability |
Tools like PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse provide both field and lab data to track these metrics. Meeting Core Web Vitals is now a confirmed ranking factor, failing them risks both SEO performance and user trust.
Faster Load Time Strengthens Brand Credibility
Speed shapes perception. When pages load quickly, users subconsciously trust the brand more; when they lag, confidence erodes before content is even consumed. This is especially critical for PR-sensitive pages like press kits, product launches, and campaign microsites.
| Case Study: Brand Speed vs. ChurnA U.S. apparel brand reduced its homepage load time from 4.8 seconds to 1.9 seconds.Result: 18% decrease in bounce rate, 12% lift in branded search CTR, and noticeable drop in churn during press coverage peaks. |
Performance isn’t just a technical layer. It’s part of your brand identity. Consistent responsiveness reinforces authority and keeps your audience engaged during high-visibility moments.
Mobile Speed Drives User Engagement and Business Growth
With over 60% of traffic coming from smartphones, mobile speed has a direct impact on business outcomes. On smaller screens, even brief tap-to-load delays lead to session loss, cart abandonment, and missed revenue.
| Industry Insight: A mobile delay of just 1s can reduce retail conversions by 20% and increase bounce rates by 32% (Google/Deloitte). |
For local businesses, eCommerce brands, and publishers, fast mobile performance is no longer a competitive edge; it’s a baseline requirement for engagement, sales, and long-term growth.

How Third-Party Scripts Affect Site Speed and Interactivity
Third-party scripts are a leading cause of long Time to Interactive (TTI) and render delays. They run outside your domain but compete for main-thread resources, which impacts JavaScript execution and blocks interactivity. Managing the impact of third-party scripts on website speed is crucial for a responsive user experience.
Analytics, Tracking, and Ad Scripts Block Main Thread Execution
Tracking scripts, such as Google Analytics, Meta Pixel, and ad networks, often cause main-thread blocking by consuming CPU cycles during page load. These scripts increase execution time, delay interactivity, and contribute to layout shifts.
In Chrome DevTools’ Performance tab, heavy third-party JavaScript often appears as lengthy scripting tasks, clearly showing their impact on render delay.
Load External Scripts Asynchronously Using Tag Managers
To reduce script-related delays, load scripts asynchronously or defer their execution. This prevents blocking the main thread during initial rendering. Google Tag Manager (GTM) consolidates tags and allows you to trigger them post-load, enhancing interactivity without compromising tracking.
| Async Script Syntax: <script src=”script.js” async></script> |
GTM Performance Benefits:
- Combines multiple tracking tags into one load
- Delays non-critical scripts until after user interaction
- Reduces render-blocking JavaScript
- Improves Time to Interactive (TTI) scores
Using GTM to load scripts asynchronously helps maintain UX speed while supporting marketing functionality.
Remove Performance-Heavy Widgets Like Live Chat and Social Embeds
Widgets like live chat, social feeds, and popups often inject iframe-heavy content that slows down rendering, increases Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), and causes Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). These elements block interactivity and degrade Core Web Vitals.
Widgets That Commonly Slow Down Sites:
- Live chat plugins (e.g., Intercom, Drift)
- Instagram, Facebook, or Twitter embed feeds.
- Review carousels and pop-up survey tools.
- Video autoplay modules in sidebars
To mitigate this, consider using click-to-load, deferred initialization, or limiting the number of widgets per page. Removing unnecessary third-party widgets can drastically improve speed and reduce abandonment.
How Does Website Speed Affect SEO, PR Campaigns, and Conversions?
Website speed directly influences search rankings, campaign reach, and conversion performance. Slow-loading pages dilute visibility, waste ad spend, and reduce ROI across both organic and paid channels. In high-stakes PR moments, speed becomes the difference between capitalizing on attention or losing it entirely.
Faster Load Times Maximize Engagement During Press Campaigns
When traffic surges during launches, promotions, or media pushes, page delays cause immediate drop-offs. Journalists, influencers, and early visitors expect instant access; any friction risks losing coverage and momentum.
| Case Example (PR Traffic Failure): A tech brand’s launch microsite buckled under press traffic, resulting in a 68% bounce rate and lost earned media links. A cached, optimized relaunch restored uptime and recovered engagement within hours. |
Fast, stable delivery keeps users on-site when attention is highest, ensuring PR-driven visits convert into shares, mentions, and sales.
High-Speed Sites Lower CPC and Improve User Trust
Page load speed affects Google Ads Quality Score, which directly impacts cost-per-click (CPC). Slow pages lower ad relevance, raise CPCs, and limit impression share.
Impact:
- A 2s delay can raise CPC by up to 50%
- Speed → Lower Bounce → Higher Quality Score → Reduced CPC
A fast site improves ad efficiency while signaling professionalism, reinforcing both campaign ROI and brand credibility.
Optimized Site Speed Boosts Leads and Sales Conversions
Delays erode trust and patience, resulting in reduced form completions, checkouts, and sign-ups. Conversion rates increase when visitors can take action immediately without waiting for elements to load.
Conversion uplift by speed tier:
| Load Time | Effect on Conversions |
| 0-2s | Highest engagement, up to +40% conversions |
| 3-4s | ~15% drop in submissions |
| 5s+ | Bounce rate spike, >30% conversion loss |
Speed doesn’t just bring visitors in. It determines whether they convert once they arrive.
How Los Angeles Public Relations Helps Optimize Website Speed
At Los Angeles Public Relations (LAPR), speed is treated as a brand infrastructure asset, not just a maintenance task. As a Los Angeles–based website optimization agency, we embed performance strategy into every layer of UX, SEO, and digital PR, ensuring that speed supports visibility, conversions, and brand credibility.
By aligning developers, strategists, and PR leads under a single speed-focused framework, LAPR enhances Core Web Vitals, ensures uptime during press surges, and maximizes the impact of both search and media campaigns.
Integrated Speed Audits in Every Digital PR Campaign
Every PR engagement begins with a launch readiness speed audit to prevent performance issues from undermining visibility. Our audits run before, during, and after campaigns to ensure sustained technical quality.
LAPR Digital PR Performance Audits Include:
- Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, FID) compliance checks
- Time to First Byte (TTFB) benchmarking
- Detection of render-blocking scripts
- Asset load sequencing and weight analysis
- Mobile responsiveness and interaction testing
This process ensures that campaign traffic is met with an instantly usable site, protecting both user trust and earned media value.
Tailored Optimization for Media-Rich and SEO-Driven Sites
Different site types require different performance strategies. LAPR tailors its approach based on the site’s content architecture, technology stack, and campaign objectives.
Example Use Cases:
- Media-Rich PR Newsroom: Using Elementor and autoplay videos:
- Collapsed sliders to reduce DOM size
- Bundled assets for fewer HTTP requests
- Enabled asynchronous loading for embedded media
- SEO-Focused SaaS Platform: Heavy JavaScript footprint:
- Migrated to cloud hosting for faster TTFB
- Deferred non-critical scripts
- Preloaded critical CSS for app-like responsiveness
This customization delivers speed without sacrificing functionality or design intent.
Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration with Dev, SEO, and UX Teams
LAPR integrates speed considerations across design, development, and marketing from the outset, avoiding the common trade-offs that occur when visual creativity compromises technical performance.
Collaborative Workflow:
- SEO defines crawl-friendly structures and Core Web Vitals targets
- Development implements async loading, asset bundling, and server caching
- UX Design ensures fast, accessible, mobile-first layouts
- PR guarantees journalist-friendly access and consistent brand delivery
This cross-team alignment turns speed into a shared responsibility, maintaining strong performance while supporting both campaign reach and brand authority.
Schedule Your Website Speed and SEO Audit with Our Los Angeles PR Team
Our Los Angeles PR team conducts thorough audits designed to identify factors that slow your site and affect SEO visibility. We analyze performance metrics and user experience signals to deliver practical insights tailored to your business goals.
What to expect from your audit:
- Review of Core Web Vitals and key speed indicators
- Assessment of technical and UX-related performance factors
- Strategic recommendations aligned with your campaign objectives
Request your audit today to uncover performance gaps and receive clear, actionable guidance; no generic reports, just focused solutions that support your digital success.





